Genetic Algorithm
Foundation
The Weather Routing Tool makes use of pymoo as the supporting library for the Genetic algorithm’s implementation.
General Concept
The genetic algorithm follows these steps (a, b):
Population Generation aka. Sampling
Reproduction: Repeat over
GENETIC_NUMBER_GENERATIONS—Selection
Crossover
Mutation
Post-processing
Repair
Remove Duplicates
Fitness Evaluation
The repeating component of the algorithm is repeated until a
termination condition is met. The termination condition can be
either the specified maximum number of generations (config.
GENETIC_NUMBER_GENERATIONS) or pre-mature termination when no valid
offsprings are produced in a generation.
Weather Routing Tool’s genetic algorithms implementation is defined in the Genetic(RoutingAlg) class definition. It utilizes the NSGAII algorithm for multi-objective optimization.
A genetic individual for the routing problem is modelled as a sequence of waypoints starting from the provided source to the destination.
References.
1. Initial Population Generation
The Initial Population critically influences the performance of the genetic algorithm. In general, the more diverse the population, the better is the genetic algorithm’s performance because the algorithm has a higher chance of reaching global optima.
The ideal population generation is a combination of various population generation methods, including:
Grid Based Population
This approach uses a deterministic approach to produce an initial population:
Breaks down the map into a set of waypoints
Shuffles the weather condition map on these waypoints to get a shuffled grid
Generates a path from source to destination using skimage’s
route_through_arraymethod to find a plausible routeRepeats this process
GENETIC_NUMBER_GENERATIONStimes to get a population poolIsofuel Population
This method utilizes the Isofuel algorithm to generate a set of routes that reach the destination. The Isofuel algorithm can be initialised with the
ISOCHRONE_NUMBER_OF_ROUTESconfiguration to generate multiple possible routes.Static Routes
These are previously generated GeoJSON files stored in a directory. These can either be manually generated or saved from another algorithm.
The system can read the directory by configuring
GENETIC_POPULATION_TYPEto “from_geojson” and setting theGENETIC_POPULATION_PATHvalue to a directory with the routes.
- Note:
The routes are expected to be named in the following format: route_{1..N}.json for example; route_1.json, route_2.json, route_3.json, …
Fallback: If a route_{i}.json file does not exist, the system falls back to generating a Great Circle Route from source to destination.
2. Reproduction
Selection
The Tournament Selection process produces N (in our case N=2) high fitness individuals that are to undergo crossover and mutation
Crossover
Crossover aims to produce two offspring from two parents such that the offspring explore a route that’s a combination of the two of parents.
When a crossover operation fails to produce feasible offspring, we can either (1) Repair the offspring in the Repair section of the code or, (2) Return the parents as is to negate this reproduction process and redo from Selection. If
GENETIC_REPAIR_TYPEis set to any valid repair strategy, Weather Routing Tool’sOffspringRejectionCrossoverwill accept all crossover attempts. If, however,GENETIC_REPAIR_TYPEis set tono_repair, crossovers will be rejected if they fail to produce feasible offsprings through the following algorithm:Generate offsprings using a child class’ implementation of the crossover function
Check if offsprings violate discrete constraints
if True — refuse both offsprings, and return the parents
if False — return offsprings
The following crossover types are implementations of
OffspringRejectionCrossover. For every crossover scenario, the algorithm chooses on a random basis which of the two approaches is executed.Single Point Crossover
Single Point Crossover is a simple approach to crossover where a single point of crossover is picked at random from both of the parents, and a route is patched from the crossover point of parent 1 to the crossover point of parent 2 and vice versa. The route patcher for the crossover can be chosen via the config variable
GENETIC_CROSSOVER_PATCHER.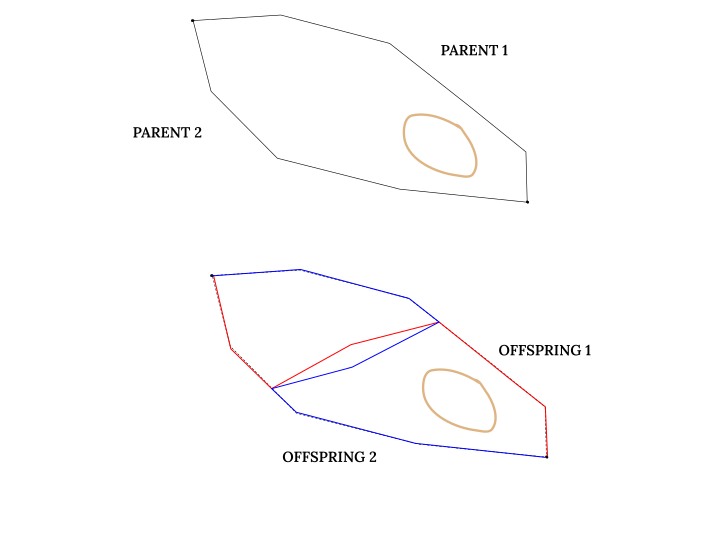
Two Point Crossover
Two Point Crossover utilizes two random points such that the patched path avoids any object that produces a constraint violation in between. As for Single Point Crossover, the route patcher can be chosen via the config variable
GENETIC_CROSSOVER_PATCHER.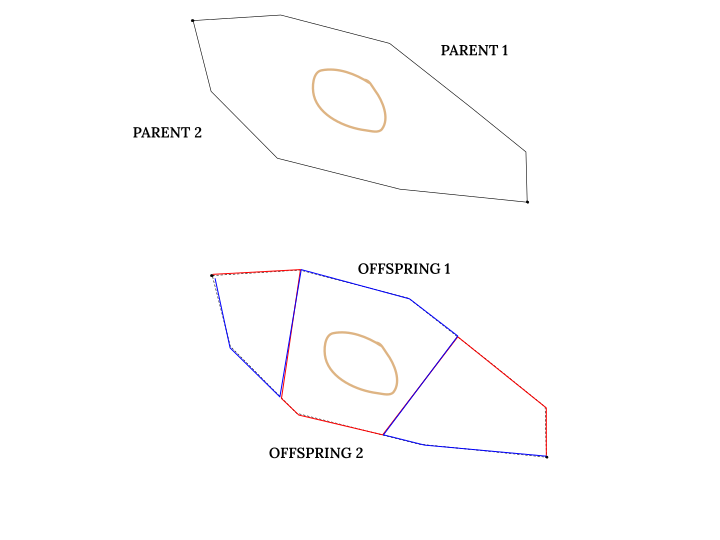
Mutation
Mutation produces unexpected variability in the initial route to introduce diversity and improve the chances of the optimum route reaching global optima.
As for
OffspringRejectionCrossover, the base classMutationConstraintRejectionrejects or accepts offspring based on the config variableGENETIC_REPAIR_TYPE. The user can choose from different mutation approaches by setting the config variableGENETIC_MUTATION_TYPE. For the settingrandom, the algorithm chooses for every mutation scenario whether route-blend or random-plateau mutation is executed. The following single mutation stategies are available:Random Walk Mutation
When looking at the waypoints as belonging to a grid, the Random Walk Mutation moves a random waypoint to one of its N-4 neighbourhood positions. Can be selected via
GENETIC_MUTATION_TYPE=rndm_walk.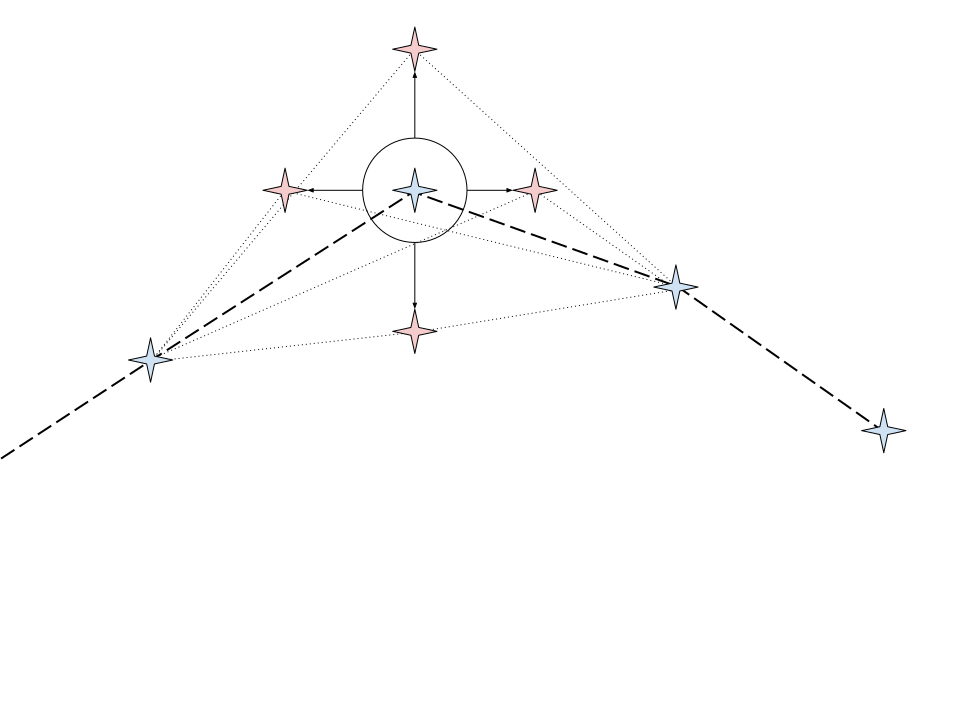
Random Plateau Mutation
A set of four waypoints is selected:
a plateau center that is chosen on a random basis,
two plateau edges which are the waypoints
plateau_size/2 waypoints before and behind the plateau center,two connectors which are the waypoints
plateau_slopebefore and behind the plateau edges.
The plateau edges are moved in the same direction to one of their N-4 neighbourhood positions as for random-walk mutation. A plateau is drawn by connecting the plateau edges to the connectors and to each other via great circle routes. Can be selected via
GENETIC_MUTATION_TYPE=rndm_plateau.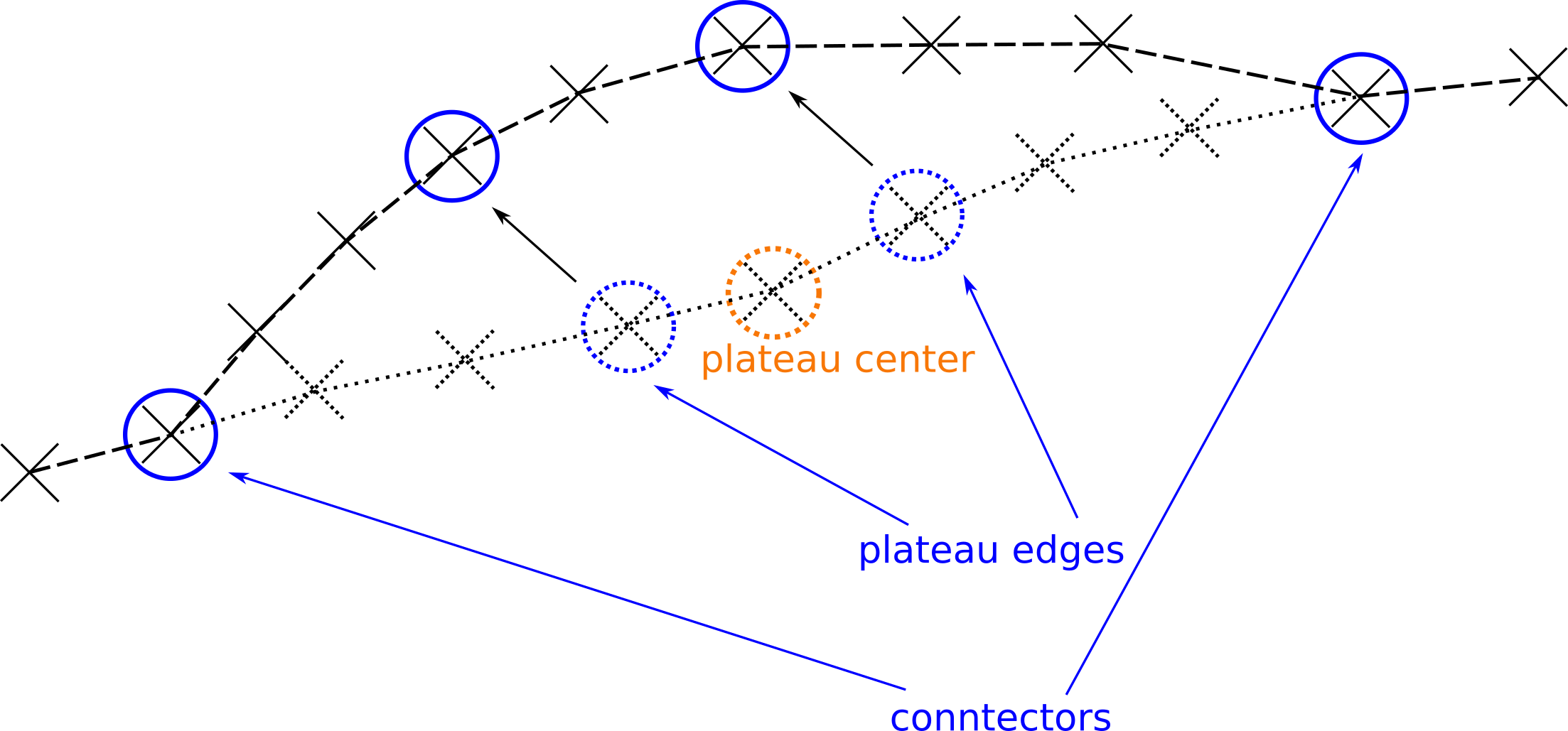
Route Blend Mutation
This process converts a sub path into a smoother route using a smoothing function such as Bezier Curves or by replacing a few waypoints using the Great Circle Route. Can be selected via
GENETIC_MUTATION_TYPE=route_blend.
3. Post-processing
Repair
The Repair classes play the role of normalizing routes and fixing constraints violations. The current implementation executes two repair processes in the following order:
Methods to repair routes are enlisted in the Route Patching section below.
WaypointsInfillRepair
Repairs routes by infilling them with equi-distant waypoints when adjacent points are farther than the specified distance resolution (gcr_dist)
This avoids long-distance jumps that may lead to impractical and unfeasible routes.
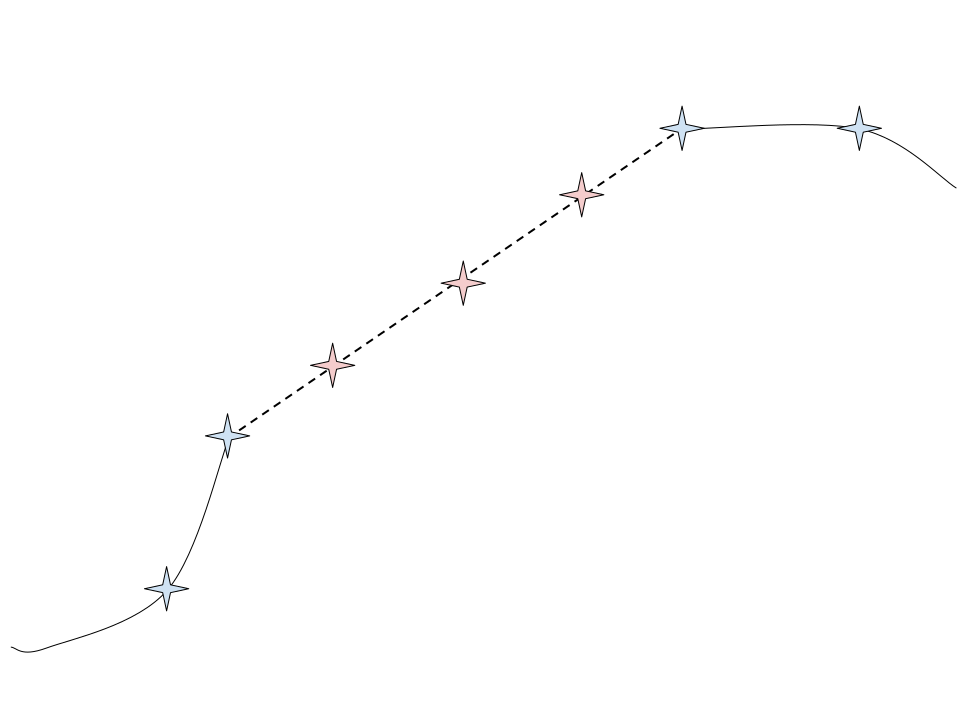

ConstraintViolationRepair
Repairs routes by identifying waypoints that are undergoing a constraint violation and finds a route around the points using the IsoFuel algorithm (See the IsoFuel Patcher in the Route Patching section below.)
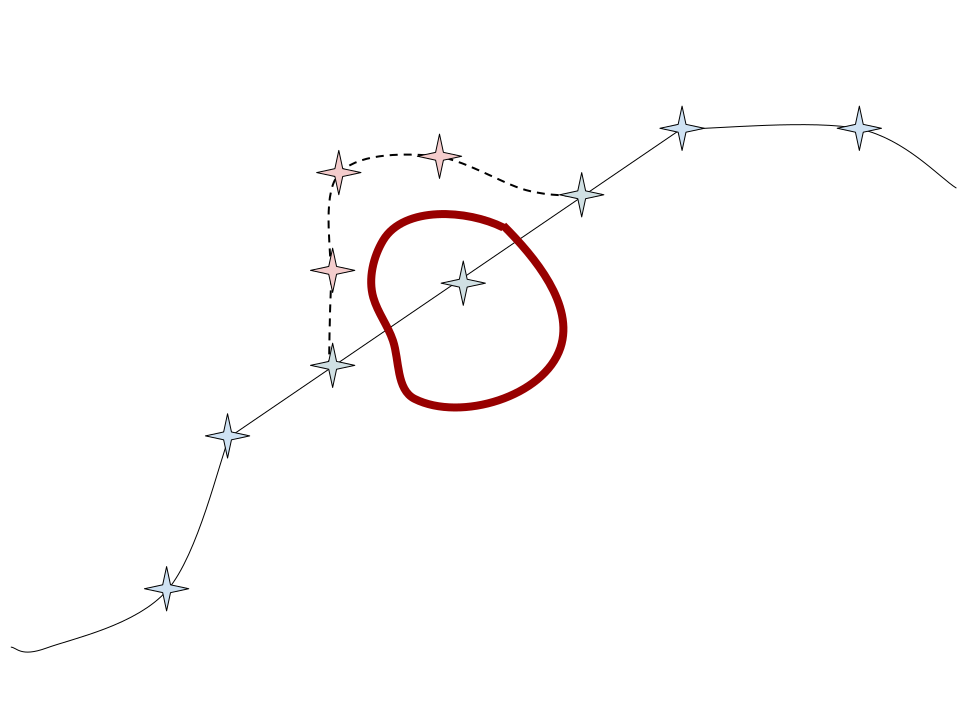

Note — Repair class’
_domethod takes in a population object and returns a population object, in both cases the size of the population should be the same as the one mentioned in the config (config.GENETIC_POPULATION_SIZE)Duplicates Removal
Pymoo gets rid of duplicate individuals in a population to maintain the diversity in the population pool. This specific function works by filtering out population individuals which are the same, thus passing on only non-repeating individuals to the next step.
Note — If duplicates remove all individuals, the entire reproduction process is repeated. Repeats can occur a maximum of a 100 times, after which the genetic algorithm reaches early termination.
4. Fitness Evaluation
RoutingProblem is Weather Routing Tool’s implementation of the route optimization problem necessary for defining the evaluation criteria for the routing problem.
The
_evaluatefunction measures the provided individual’s fitness F and the constraints G .
Fitness (F) — is a list of floats representing the fitness evaluation of the individual per objective (fuel, distance, etc.)
Constraints (G) — is a list of floats represents the total constraint violations per constraint (specified by the
constraints_listvalue)
Route Patching
Route Patching is an important concept that comes up as a necessity across the genetic implementation. This system has uses within Crossover, Mutation, and Repair functions.
The purpose of a Route Patcher is to find a valid feasible route from point A to point B, without necessarily optimising the produced sub-path.
A Route Patcher works well if
it produces valid feasible routes and
if it can find novel ways to connect waypoints.
Weather Routing Tool’s Route Patcher uses the following ways to connect waypoints:
Great Circle Route
Produce a granular route along the great circle distance connecting the two points.
Advantages —
Produces the shortest best route from point A to point B.
Disadvantages —
It cannot handle complex route navigation, e.g., if there’s a landmass in between the waypoints, the patched route will violate constraints and will be discarded during evaluation. It is left to the calling function to update the waypoints.
Isofuel Algorithm
Produce an optimum sub-route using the Isofuel algorithm.
Advantages —
Produces an optimal route navigating complexities.
Disadvantages —
Can be very slow and can fail based on the isofuel configuration. In case of failing, the algorithm will fall back to patching via the great circle route.
Can be used if —
We parallelize the execution of the Isofuel algorithm to speed up the process.
Implementation Notes:
The intuition behind having Route Patching implementations setup as classes follows the following:
a. Route patching can be quite expensive during both the preparation (defining map, loading configs, etc.) and the execution stage (patching between point A and point B). An Object Oriented implementation of the same helps separate the two processes, avoids redundancy and can contribute to the overall speed in the longer run.
b. Implementation consistency makes it easier to swap between different Patching implementations and maintains clean code
Config Parameters
GENETIC_NUMBER_GENERATIONS— Max number of generations.GENETIC_NUMBER_OFFSPRINGS— Number of offsprings.GENETIC_POPULATION_SIZE— Population size of the genetic algorithm.GENETIC_POPULATION_TYPE— Population generation method for the. genetic algorithmGENETIC_POPULATION_PATH— Path to population directory when.GENETIC_POPULATION_TYPEis “from_geojson”
GENETIC_REPAIR_TYPE- Repair strategy for genetic algorithm.GENETIC_MUTATION_TYPE- Mutation strategy.GENETIC_CROSSOVER_PATCHER- Patching strategy for crossover.GENETIC_FIX_RANDOM_SEED- Handling of random seed.
For more details on the configuration variables, please check the general section on Configuration.